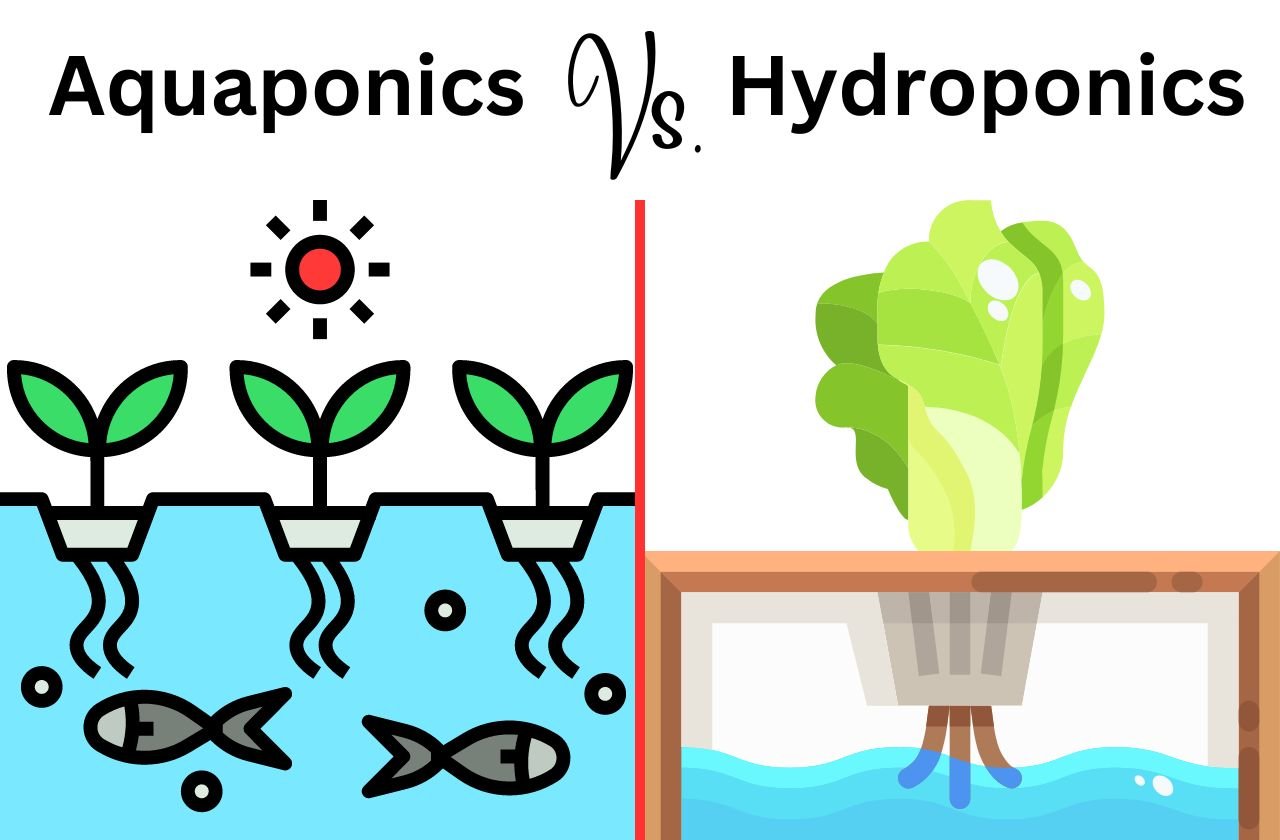
Aquaponics Vs. Hydroponics
I get commissions for purchases made through links in this post. View our Affiliate Disclaimer.
Homesteaders are always looking for a way to maximize their food production, and hydroponics and aquaponics are two popular methods for achieving this goal. How do these two food creation systems compare, and which should you choose for your homestead or to increase your food security?
Aquaponics and hydroponics are soilless growing systems where hydroponics focuses on growing plants, while aquaponics incorporates fish raising in the equation. Aquaponics is better for a self-sustaining system but is more complex than hydroponics. Both systems require careful monitoring.
Whether you are an aspiring gardener, an environmental enthusiast, or simply curious about sustainable food production practices, we will provide valuable insights into aquaponics and hydroponics. This will help you decide which option best suits your needs and how you can use the possibilities offered by these innovative cultivation techniques.
Aquaponics Vs. Hydroponics Compared
Aquaponics and hydroponics share similarities in that both systems eliminate the need for soil and rely on water as the primary medium for plant growth. However, they differ in the way they provide essential nutrients to plants.
Aquaponics combines aquaculture (fish farming) and hydroponics, creating a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants.
Hydroponics, on the other hand, directly provides plants with nutrient-rich water solutions. These soilless cultivation techniques offer unique advantages and revolutionize how we grow plants and produce food sustainably.
Aquaponics and hydroponics offer efficient solutions that can be implemented in various environments, including urban areas with limited space. Both systems have the potential to yield higher crop outputs while minimizing resource usage and environmental impact.
What Is Aquaponics?

Aquaponics is a unique and fascinating farming method that combines aquaculture and hydroponics, creating a mutually beneficial relationship between fish and plants. In this section, we will explore the intricacies of aquaponics, including its components and how it operates.
Aquaponics is a closed-loop system that mimics a natural ecosystem. It involves cultivating plants and rearing aquatic animals in a symbiotic environment, usually fish.
The basic principle of aquaponics is the conversion of fish waste into plant nutrients through a natural filtration process.
The process begins with a fish tank where the fish are kept. The fish produce waste, mainly in the form of ammonia, through their excretions. Ammonia is toxic to fish but is a valuable source of plant nutrients.
To remove the toxic ammonia, a key component in aquaponics is the beneficial bacteria. These bacteria, known as nitrifying bacteria, convert the ammonia into nitrites and then into nitrates, which are less harmful to the fish. Nitrates are also more easily absorbed by plants as nutrients.
The nutrient-rich water from the fish tank is pumped into the grow beds or containers where the plants are grown. The plants extract the nutrients from the water, effectively filtering and purifying it for the fish. As the water circulates through the grow beds, it becomes oxygenated, benefiting both the plants and the fish.
The clean water is then returned to the fish tank, completing the cycle. This continuous flow of water ensures a sustainable and balanced environment for aquatic animals and plants.
Key Components Of Aquaponics And Their Functions

Aquaponics systems consist of several essential components, each playing a vital role in creating a successful and harmonious ecosystem.
- Fish Tank. This is where the aquatic animals, usually fish, are kept. The size and type of fish chosen depend on various factors such as climate, system size, and desired outcomes.
- The Grow Bed. The grow bed is where the plants are cultivated. It can be filled with a medium like gravel, expanded clay pellets, or coconut coir, providing support for the plant’s root systems. The grow bed also acts as a filter, removing excess nutrients from the water. The grow bed is usually an implementation of a hydroponic growing system.
- Water Pump. The water pump is responsible for circulating the water between the fish tank and the grow beds. It ensures a continuous flow of nutrient-rich water for the plants and helps oxygenate the water.
- Beneficial Bacteria. These bacteria are crucial for the conversion of ammonia into nitrites and nitrates. They colonize the grow beds, the surface area of the gravel or other medium, and the roots of the plants. The presence of these bacteria is essential for maintaining a healthy and balanced aquaponic system.
Advantages Of Aquaponics
Aquaponics offers several advantages over traditional farming methods and even standard hydroponic growing systems.
- Natural Fertilization. The fish waste provides a natural and organic source of nutrients for plants, eliminating the need for synthetic fertilizers. This leads to healthier and more nutritious produce.
- Sustainability and Resource Efficiency. Aquaponics is incredibly resource-efficient as it recirculates water, reducing water usage by up to 90% compared to traditional farming. The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants creates a self-sustaining ecosystem that requires fewer inputs.
- Integration of Fish and Plant Cultivation. Aquaponics allows for the simultaneous cultivation of both fish and plants in a compact system. This integration maximizes space utilization and promotes a more holistic approach to farming.
Aquaponics presents an innovative and environmentally friendly method of food production. Its ability to grow a wide range of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, and even some fruits, makes it a versatile option for both home gardeners and commercial farmers.
With a solid understanding of aquaponics, we can now move on to exploring hydroponics and how it compares to aquaponics.
What Is Hydroponics

Hydroponics is a soilless cultivation technique that focuses on delivering nutrients directly to plant roots through a water-based solution. In this section, we will delve into the fundamentals of hydroponics, including its principles and various types of hydroponic systems.
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a controlled environment without the use of soil. Instead, plants are placed in an inert medium such as perlite, Rockwool, or coconut coir, which provides support for the roots while allowing the nutrient solution to reach them.
The nutrient solution, consisting of water and a balanced mix of essential nutrients, is directly delivered to the plant roots. This allows for precise control over nutrient levels, pH, and other environmental factors that affect plant growth. The roots have constant access to oxygen, promoting efficient nutrient uptake.
Unlike traditional soil-based farming, where plants must allocate energy to develop extensive root systems for nutrient acquisition, hydroponics provides plants with readily available nutrients. This results in faster growth rates, increased yields, and more efficient resource utilization.
Types Of Hydroponic Systems
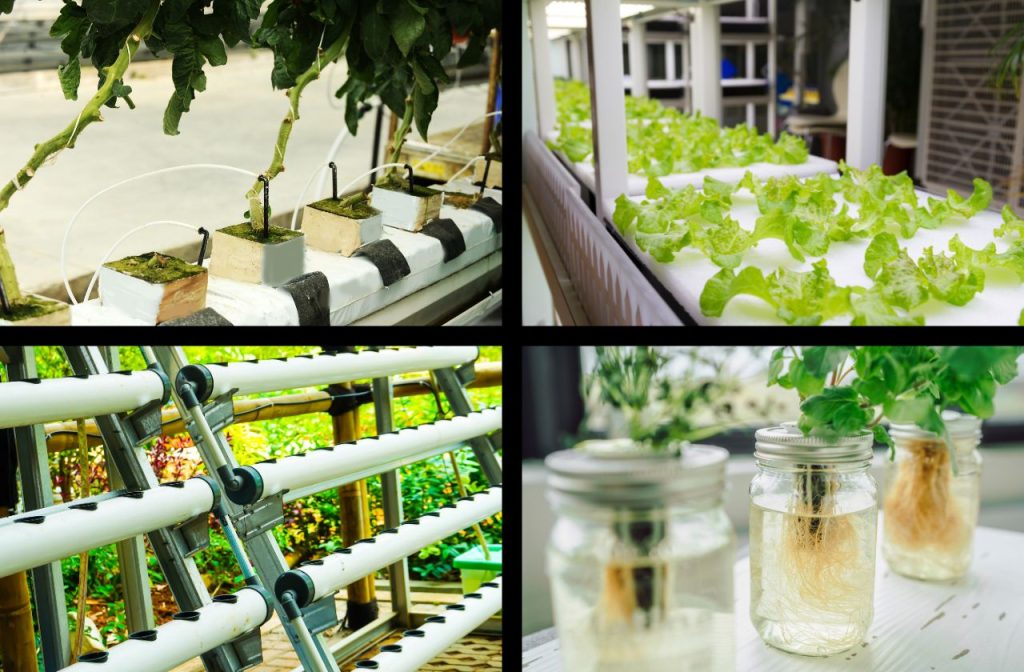

Hydroponic systems come in various forms, each offering unique advantages and suitability for different applications. Some common types of hydroponic systems include the following.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT). NFT is a system where a thin film of nutrient-rich water continuously flows over the bare roots of the plants, typically through a sloped channel. The roots absorb the necessary nutrients, and the excess solution is collected and recirculated.
Deep Water Culture (DWC). DWC involves suspending the plant roots directly in the nutrient solution, allowing constant contact with oxygenated water. The plants are typically held in net pots with their roots submerged, and an air pump provides oxygen to the solution.
Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain). In the ebb and flow system, plants are placed in grow trays filled with an inert medium. Periodically, the trays are flooded with the nutrient solution, which is then drained back into a reservoir. This cycle provides oxygenation to the roots and prevents waterlogging.
These are just a few examples of hydroponic systems, and there are many other variations and hybrid approaches available. The choice of system depends on factors such as available space, crop type, desired level of automation, and personal preference.
Advantages Of Hydroponics
Hydroponics offers several advantages over traditional soil-based agriculture, as well as some unique benefits when compared to aquaponics:
- Precise Control over Nutrient Levels. Hydroponics allows growers to have precise control over the nutrient composition and concentration delivered to the plants. This optimization ensures that plants receive an ideal balance of nutrients for optimal growth and productivity.
- Faster Growth and Higher Yields. With direct access to readily available nutrients and oxygen, plants in hydroponic systems can grow up to 25% faster than in soil-based systems. The controlled environment and optimized nutrient delivery also contribute to higher crop yields.
- Flexibility in Location and Setup. Hydroponics can be implemented in various settings, from small-scale indoor gardens to large commercial operations. Its flexibility allows for year-round cultivation, regardless of geographical location or seasonal limitations.
Hydroponics has gained popularity due to its efficient use of resources, higher productivity, and the ability to grow crops in unconventional environments. It has become a preferred choice for urban farming, vertical farming, homesteaders, and sustainable agriculture initiatives.
Comparison Of Aquaponics And Hydroponics
Aquaponics and hydroponics are two distinct soilless cultivation systems with their own unique characteristics and advantages.
We will compare and contrast these systems based on various factors, including nutrient source and management, environmental impact, maintenance requirements, cost considerations, and crop variety.
Nutrient Source And Management
In aquaponics, the nutrients for plant growth are derived from the waste produced by the fish in the system. The fish excrete ammonia, which is converted into nitrates by beneficial bacteria.
These nitrates serve as the primary nutrient source for the plants. Aquaponics relies on the balance between fish health and plant nutrition.
In hydroponics, the nutrients for plant growth are provided through a synthetic nutrient solution. Growers have complete control over the nutrient composition and concentration, allowing for precise adjustments to meet the specific needs of different plant species.
Nutrient management involves monitoring and adjusting the nutrient solution to maintain optimal levels for plant growth.
Environmental Impact
Aquaponics has a relatively low environmental impact. It conserves water by recirculating it within the system, reducing water usage compared to traditional farming methods.
The system also minimizes the need for synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, promoting organic and sustainable practices.
Hydroponics is known for its water efficiency, using up to 90% less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. However, hydroponic systems rely on synthetic nutrient solutions, which require energy-intensive production processes.
The disposal of used nutrient solutions can also pose environmental challenges if not managed properly.
Maintenance And System Complexity
Aquaponic systems require careful management of both the fish and plant components. Maintaining fish health and water quality is crucial, which involves monitoring ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels, as well as temperature and oxygen levels. Additionally, periodic testing of pH and nutrient levels is necessary to ensure optimal plant growth.
Hydroponic systems generally require less maintenance compared to aquaponics. Monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels, pH, and water temperature are the primary maintenance tasks. Regular monitoring of plant health, disease prevention, and pest management are also important aspects of hydroponic system maintenance.
Cost Considerations
Aquaponics systems can have higher initial setup costs due to the need for fish tanks, grow beds, water pumps, and plumbing infrastructure.
Additionally, there are ongoing costs associated with fish feed and potential expenses for managing fish health. However, the potential for selling both fish and plant products can offset some of these costs.
Hydroponics systems typically have lower initial setup costs compared to aquaponics. The main expenses include setting up the infrastructure, acquiring grow trays or containers, purchasing nutrient solutions, and investing in lighting and ventilation for indoor setups.
Ongoing costs for hydroponic systems include the purchase of nutrient solutions and maintenance supplies.
Crop Variety And Plant Choices

Aquaponics is well-suited for cultivating leafy greens, herbs, and certain fruiting plants that have lower nutrient demands.
It may not be suitable for plants with high nutrient requirements or crops that prefer specific pH or nutrient conditions. However, with proper adjustments to the system, a wide range of plants can be grown successfully.
Hydroponics offers flexibility in growing a wide variety of crops, including leafy greens, herbs, fruits, vegetables, and even flowers. The controlled environment and precise nutrient delivery enable growers to tailor the conditions to meet the specific requirements of different plant species.
By considering these factors, you can make informed decisions about whether aquaponics or hydroponics is the right choice for their specific circumstances, goals, and resources.
Both systems offer sustainable and efficient alternatives to traditional soil-based agriculture, promoting resource conservation and maximizing crop productivity.
Choosing Between Aquaponics And Hydroponics
Choosing between aquaponics and hydroponics depends on various factors such as personal preferences, resources, goals, and available space. In this section, we will provide some practical tips and considerations to help you make an informed decision about which system is the right fit for you.
Consider Your Goals and Objectives
Getting a handle on your motives, goals, and objectives for producing your own food will be a key aspect of choosing between aquaponics and hydroponics.
- Food Production. Determine the primary purpose of your system. Are you looking to grow vegetables, herbs, or fruits for personal consumption, or do you have commercial aspirations? Aquaponics and hydroponics can both fulfill these goals, but the scale and complexity of the system may vary.
- Sustainability. Aquaponics might be a better choice if sustainability and organic practices are a priority. The symbiotic relationship between fish and plants in aquaponics promotes resource efficiency, eliminates the need for synthetic fertilizers, and reduces environmental impact.
- Learning Experience. If you are interested in understanding the intricacies of natural ecosystems and want a more hands-on learning experience, aquaponics offers a unique opportunity to observe the interplay between fish, bacteria, and plants.
Assess Your Available Resources
The resources available to you may be a limiting factor and contribute to your decision regarding the best food production system that matches your circumstances and resource availability.
- Space. Evaluate the available space for your system. Hydroponics can be set up indoors or outdoors, utilizing vertical space with systems like vertical towers or utilizing horizontal space with systems like NFT or DWC. Aquaponics typically requires more space due to the inclusion of fish tanks and the need for fish habitat.
- Water Supply. Both aquaponics and hydroponics require a reliable water supply. Assess the availability and quality of water in your location. Keep in mind that aquaponics involves water recirculation, so water quality and filtration are crucial for maintaining fish health.
- Availability of a reliable power source. Many hydroponic systems can be run with limited electricity or in unreliable electricity environments. A steady electricity supply is crucial for aquaponics to work correctly and keep the fish alive.
- Budget. Consider your budget for the system setup and ongoing maintenance. Aquaponics systems tend to have higher initial costs due to the need for fish tanks, filters, and additional infrastructure. Hydroponic systems can be more cost-effective initially, but ongoing expenses such as nutrient solutions should be factored into the budget.
Evaluate Maintenance Requirements Of Aquaponics And Hydroponics
Maintenance is key to keeping the systems functional and operating within the required parameters to promote growth.
- Time Commitment. Assess the time you can dedicate to system maintenance. Aquaponics systems require regular monitoring of water quality, fish health, and nutrient levels. Hydroponic systems also require monitoring and adjusting nutrient levels, pH, and plant health, but the time commitment is generally less than aquaponics. Determine the level of involvement you are comfortable with.
- Technical Expertise. Evaluate your knowledge and experience in managing fish and plants. Aquaponics may require a deeper understanding of fish care, water chemistry, and bacteria management. Hydroponics generally has a shallower learning curve and is more accessible to beginners.
Seek Local Support and Resources
Look for local aquaponics or hydroponics communities, groups, or experts who can provide guidance and support. Local resources can provide valuable insights into climate considerations, crop selection, and potential challenges specific to your region.
Consider attending workshops, courses, or seminars to enhance your understanding of aquaponics or hydroponics. Hands-on training can boost your confidence and equip you with practical knowledge for successful system management. Remember that choosing between aquaponics and hydroponics is not a binary decision. You can also explore hybrid systems that combine elements of both methods to suit your specific needs and preferences.
Practical Tips And Guidelines For Setting Up And Maintaining Your Chosen System
Setting up and maintaining your chosen aquaponics or hydroponics system requires careful planning and attention to detail. This section will provide practical tips and guidelines to help you ensure a successful and productive soilless farming experience.
- Research and Design. Conduct thorough research and understand the specific requirements of your chosen system. Consider factors such as the size and type of system, suitable plant varieties, nutrient solutions, lighting, and ventilation.
- Start Small. If you are new to soilless farming, it is advisable to start with a small-scale system to gain experience and understanding. You can gradually expand and scale up as you become more proficient.
- Water Quality. Ensure that your water source is of good quality and free from contaminants. Conduct water tests for pH, hardness, and heavy metal content to ensure it meets the requirements of your chosen system.
- Temperature Control. Maintain optimal temperature levels for both plants and fish (in aquaponics systems) to promote healthy growth. Consider using heaters, coolers, or insulation to regulate temperature fluctuations, especially in outdoor or greenhouse setups.
- Nutrient Solution Preparation. Follow manufacturer instructions or established formulas to prepare the nutrient solution for hydroponic systems. Adjust nutrient concentrations and pH levels based on the specific needs of your chosen crops.
- Testing and Monitoring. Regularly monitor and adjust nutrient levels, pH, and electrical conductivity (EC) using appropriate testing kits. This helps ensure that plants receive the correct balance of nutrients for optimal growth.
- Nutrient Solution Changes. Replace the nutrient solution periodically to prevent nutrient imbalances and the accumulation of toxins. The frequency of solution changes depends on the system size, crop type, and environmental conditions.
- Water Quality and Filtration. In aquaponics systems, maintain excellent water quality for the fish and plants. Use filtration systems, such as mechanical filters, biofilters, and clarifiers, to remove solids, maintain water clarity, and promote fish health.
- Fish Care. If you have an aquaponics system, pay close attention to the health and well-being of the fish. Regularly monitor ammonia, nitrite, and nitrate levels to ensure a stable and healthy environment for the fish and nutrient availability for the plants.
- Pest and Disease Management. Implement preventive measures such as proper sanitation, regular plant inspections, and integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to minimize the risk of pests and diseases. Promptly address any issues to prevent them from spreading.
- Lighting and Ventilation. Provide adequate lighting and proper air circulation in indoor setups to ensure optimal plant growth. Use appropriate grow lights and fans to mimic natural lighting conditions and prevent the buildup of heat and humidity.
- Stay Informed. Stay updated on the latest advancements, research, and best practices in aquaponics or hydroponics. Join online forums, attend workshops, and connect with fellow growers to exchange knowledge and learn from their experiences.
- Record Keeping. Maintain a journal or logbook to record observations, changes made to the system, and crop performance. This information will help you identify trends, troubleshoot issues, and make informed adjustments in the future.
- Experiment and Innovate. Embrace experimentation and innovation in your system. Try different plant varieties, nutrient formulations, or system modifications to optimize performance and find what works best for your specific setup.
Remember, setting up and maintaining an aquaponics or hydroponics system requires patience, attention to detail, and ongoing commitment. Regular monitoring, timely adjustments, and continuous learning will contribute to the long-term success of your soilless farming endeavor.
By following these practical tips and guidelines, you are well on your way to enjoying the benefits of growing fresh, healthy crops in a controlled and efficient manner.
Good luck with your aquaponics or hydroponics journey, and may your soilless farming adventures be fruitful and rewarding!
Conclusion
Aquaponics and hydroponics are both innovative and sustainable soilless cultivation methods offering unique benefits for growing food. Each system has its own characteristics, advantages, and considerations that make them suitable for different individuals and situations.
When choosing between aquaponics and hydroponics, it is important to consider your goals, available resources, maintenance requirements, and personal preferences. Assess factors such as space availability, water supply, budget, time commitment, and technical expertise.
Whether you opt for aquaponics or hydroponics, embracing soilless cultivation methods can contribute to sustainable food production, resource conservation, and the cultivation of fresh and healthy crops. By making an informed decision and following the best practices for system setup and maintenance, you can embark on an exciting journey of growing your own food and contributing to a more sustainable future.
Get more posts like this
Subscribe to our mailing list and get interesting homesteading and green living info and updates to your email inbox.
Thank you for subscribing.
Something went wrong.